Published in Royal Society Open Science, Vorombe titan (meaning ‘big bird’ in Malagasy and Greek), has taken the title.
The bird weighed up to 800 kg and three metres tall, with the research also discovering unexpected diversity Madagascan creatures.
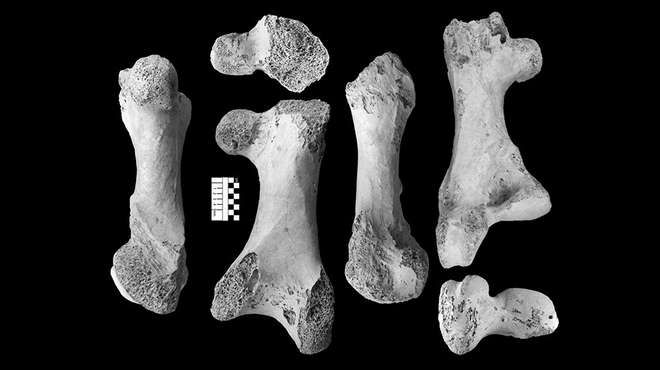
Until now, it was previously suggested that up to 15 different species of elephant birds had been identified under two genera, however research by ZSL scientists boasts new rigorous and quantitative evidence – that shows, in fact, this is not the case. Armed with a tape measure and a pair of callipers, hundreds of elephant bird bones from museums across the globe to uncover the world’s largest bird, while also revealing their taxonomy is in fact spread across three genera and at least four distinct species; thus, constituting the first taxonomic reassessment of the family in over 80 years.
Elephant birds (belonging to the family Aepyornithidae) are an extinct group of colossal flightless birds that roamed Madagascar during the Late Quaternary, with two genera (Aepyornis and Mullerornis) previously recognised by scientists. The first species to be described, Aepyornis maximus, has often been considered to be the world’s largest bird. In 1894, British scientist C.W. Andrews described an even larger species, Aepyornis titan, this has usually been dismissed as an unusually large specimen of A. maximus. However, ZSL’s research reveals Andrew’s ‘titan’ bird was indeed a distinct species. The shape and size of its bones are so different from all other elephant birds that it has now been given the new genus name Vorombe by ZSL.
Lead Author at ZSL’s Institute of Zoology, Dr James Hansford said:
“Elephant birds were the biggest of Madagascar’s megafauna and arguably one of the most important in the islands evolutionary history – even more so than lemurs. This is because large-bodied animals have an enormous impact on the wider ecosystem they live in via controlling vegetation through eating plants, spreading biomass and dispersing seeds through defecation. Madagascar is still suffering the effects of the extinction of these birds today.”
“Without an accurate understanding of past species diversity, we can’t properly understand evolution or ecology in unique island systems such as Madagascar or reconstruct exactly what’s been lost since human arrival on these islands. Knowing the history of biodiversity loss is essential to determine how to conserve today’s threatened species.”
Analysing this data in a novel combination of machine learning combined with Bayesian clustering, Dr Hansford applied modern techniques to solve a 150-year-old taxonomic knot, that will form the modern understanding of these enigmatic avian megafauna.




